Technical notes
XML_instances
This instances are parsed, and prepared to be converted into CSV files. Moreover, two temporary folders are created: Meta-INF and reports.
Meta-INF contains the JSON report package, and reports folder contains the variables belonging to the EBA´s taxonomy modules, filing indicators and
parameters. All of those are CSV files.
Conversion process
The conversion process have the following steps:
1º: First step is to identify the
XML instancemodule. For eachfactcontain in the instance, EBA’s metric and referencecontextare identified.2ª: With the objects identified,
Scenarioassociated to that referenceContextis read, andvariableIDcodes withinindex.jsonare searched to associate them to values founded in the Scenario and the EBA’s metric value.3º: In case
open keysare found in thetableassociated to that metric, each value will have a new column containing them.4ª: All the previous process is done by doing an inner join, where data contained in each instance table is process in a pandas dataframe, and each
scenariowith their referencecontextsassociated in another pandas dataframe.5º: Finally, an inner join is done between the references
contextscontained in each pandas dataframe, and obtain the variable id.
Here is a conversion example with open Keys:
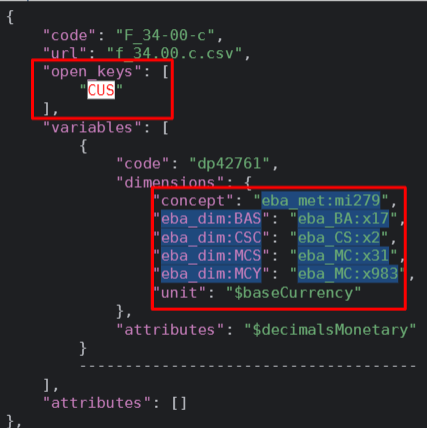
Firstly, CUS open key is founded in the information contained in the module. As picture shows, the variables dimensions contained in the preprocessed JSON are selected:
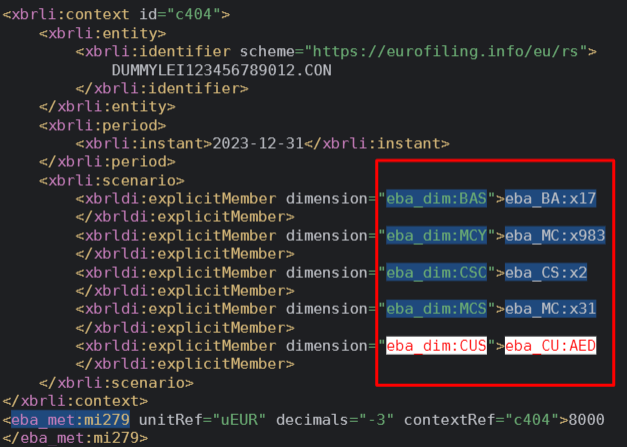
Secondly, in the instance, we read the scenario and look for the same values:
Workarounds
Due to the design of XBRL-CSV, some workarounds had to be made in the parameters file:
baseCurrency: It can only be one (e.g: EUR). It is taken from the first value of the instance.
decimalsInteger: It will take te maximum value from the ones reported. Default value is 0.
decimalsMonetary: It will take the maximum value from the ones reported. Default value is 0.
decimalsPercentage: It will take the maximum value from the ones reported. Default value is 4.
Load Taxonomy
Firstly, EBA´s taxonomy is loaded by using the following function contained in the API package:
python taxonomy_loader.py --input_path FullTaxonomy.7z
When it is loaded, the URL reference of the modules contained within the taxonomy are saved in a JSON file called index.json,
which is generated in this process. At this point, all modules can be called by using its specific URL reference, so all of
its tables and variables are available. Therefore, index.json file is the main source in this loading process, as it will hold
all the information related to EBA’s taxonomy and call it in an easily way.
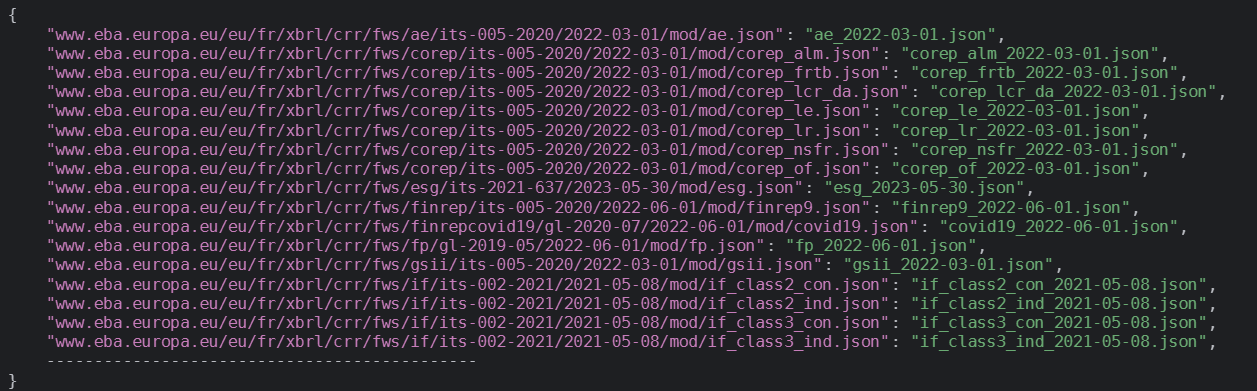
Index.json will look like this:
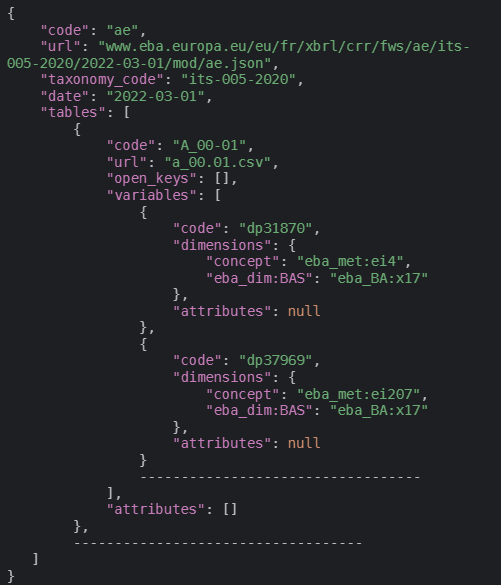
Also, each module has its own file with all information we need:
Secondly, XBRL-XML instances have to be loaded. To do that, API package contains the following function:
>>> from xbridge.api import load_instance
>>> instance: Instance = load_instance(input_path)